How to Design for Injection Molding: Essential Tips for Success
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, "design for injection molding" has emerged as a crucial consideration for engineers and product developers seeking to optimize production efficiency and product quality. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global injection molding market is expected to reach $350 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand across several sectors, including automotive, consumer goods, and healthcare. This growth underscores the importance of understanding the intricacies of design specific to injection molding processes, which can significantly impact both production costs and timelines.

To achieve successful outcomes, it is vital to adhere to essential design principles that cater to the unique characteristics of injection molding. Factors such as material selection, wall thickness, and mold design play a pivotal role in ensuring that the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) highlights that inefficient design practices can lead to common pitfalls, such as increased cycle times and post-production defects, which can ultimately affect profitability. By prioritizing a well-informed design approach, manufacturers can enhance not only the resilience and performance of their products but also their competitive edge in a saturated market.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Injection Molding Design
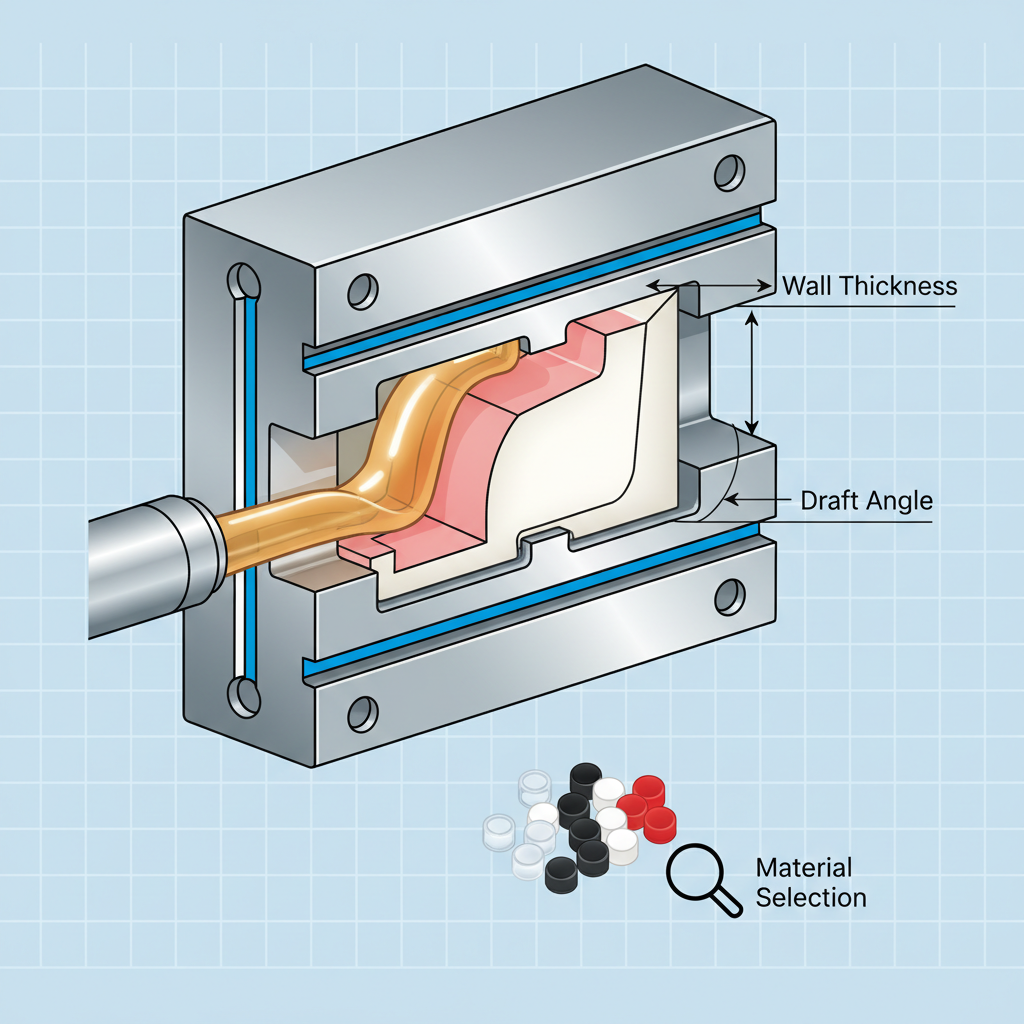
Designing for injection molding requires a solid grasp of its foundational principles. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for creating efficient, manufacturable designs. Key factors include material selection, wall thickness, and draft angles. Choosing the right material helps in achieving the desired properties while ensuring compatibility with the molding process.
When it comes to wall thickness, maintaining uniformity is essential to prevent warping and uneven cooling. Thicker walls can lead to longer cycle times and increased production costs. A good practice is to adhere to industry standards, which typically recommend a wall thickness ranging from 1 to 3 mm, depending on the material and part size.
Another important aspect is the incorporation of draft angles in your design. Draft angles facilitate the removal of the part from the mold and minimize the risk of damage. A standard draft angle of 1 to 2 degrees is often sufficient, but may vary based on the complexity of the part. By paying close attention to these details, designers can improve manufacturability and reduce production issues, setting the stage for success in injection molding.
Key Considerations for Material Selection in Injection Molding
When designing for injection molding, selecting the right material is crucial for achieving the desired quality and functionality of the final product. Key considerations include the material's mechanical properties, thermal stability, and compatibility with the injection molding process. Each type of plastic offers unique benefits; for instance, ABS is well-known for its strength and rigidity, while polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and flexibility. Understanding these properties aids in making informed decisions that align with the product's intended use.
Tip: Always consider the end-use environment of the product. If the component will be exposed to harsh chemicals or high temperatures, selecting a material with corresponding resistance is vital. Additionally, the cost of materials should be balanced with performance requirements to ensure feasibility in large-scale production.
Another critical aspect of material selection is processing behavior, which can influence cycle times and production efficiency. Materials like nylon may require drying before processing to prevent defects, while others might flow better under heat and pressure. Evaluating these factors will help streamline production and minimize potential issues.
Tip: Engage with material suppliers to gain insights on material performance and typical applications. This collaboration can provide valuable perspectives that enhance your design process and lead to better outcomes in injection molding.
Best Practices for Designing Mold Features and Tolerances
Designing for injection molding requires a keen understanding of mold features and tolerances to ensure the final product meets its intended design and functionality. According to a report from the Society of Plastics Engineers, around 90% of injection molding defects are attributed to poor design choices—underscoring the importance of getting it right from the start.
When considering mold features, it’s essential to focus on the wall thickness. A standard recommendation is to maintain uniform wall thickness to avoid issues like warping and sink marks. Aim for a thickness of about 1-3mm, depending on the specific material properties. Additionally, the design should incorporate proper draft angles, typically 1-3 degrees, to facilitate easy ejection of the part from the mold.
Tolerances play a crucial role as well. The standard tolerance for injection molded parts is typically ±0.5% per inch. Designers should always account for these tolerances during the initial design phase, as deviations can lead to costly adjustments and rework. Implementing best practices, such as using fit and clearance designs, can greatly enhance the precision and quality of the final molded product.
Strategies for Optimizing Production Efficiency in Injection Molding
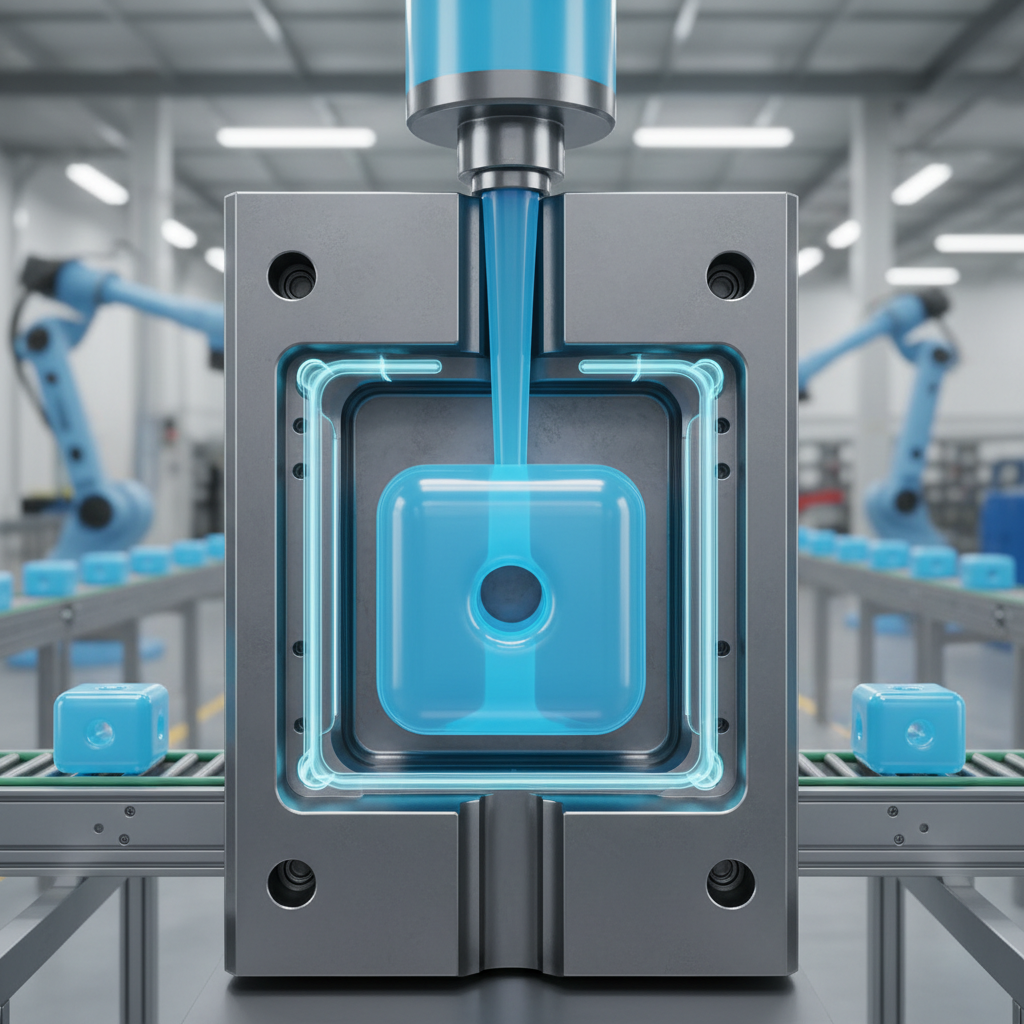
When it comes to optimizing production efficiency in injection molding, careful design is key. A well-thought-out design not only improves the manufacturing process but also enhances the overall quality of the final product. One essential strategy is to minimize the complexity of the part design. Simpler geometries are easier to mold, which can significantly reduce cycle times and increase throughput.
Another crucial tip is to consider the gate placement strategically. Proper gate location can help ensure optimal material flow and reduce issues like warping or sink marks. Placing gates where they allow for even filling while avoiding excessive pressure drop can enhance the part quality and lead to faster production rates.
Additionally, selecting the right materials is vital for both performance and efficiency. Understanding the flow characteristics of the chosen resin can help you design more effective molds that function reliably at higher speeds. By balancing material properties with design considerations, you can streamline the injection molding process and achieve better production results.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Injection Molding Design Process
Injection molding can be a highly effective manufacturing method, but there are several common pitfalls that designers must avoid to ensure successful outcomes. One major mistake is neglecting the importance of draft angles. Insufficient draft can lead to parts getting stuck in molds, causing delays and potential damage to the product. Designers should aim for a minimum of 1-3 degrees of draft, depending on the material and part geometry, to facilitate smooth ejection from the mold.
Another critical issue to watch out for is the improper distribution of wall thickness. Uneven thickness can result in warping, sink marks, or even incomplete filling of the mold. Designers should strive for consistent wall thickness to ensure uniform cooling and minimize stress during the molding process. Additionally, incorporating features such as ribs or gussets can help to maintain structural integrity without sacrificing material efficiency. By being mindful of these pitfalls, designers can enhance the overall quality and reliability of their injection-molded parts.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Design for Injection Molding in 2025
-

Understanding Injection Molding Tooling Processes and Their Industry Impact
-

Envisioning Tomorrow: The Role of Polypropylene Plastic in Sustainable Manufacturing
-

Exploring the Versatility of PVC Sheets: Innovative Applications You Didn't Know About
-

2025 Top 10 Innovations in Injection Moulding Process: Boost Efficiency by 30%+
-
Exploring the Versatility of PVC Plastic: Innovative Applications in Modern Design
