Top 10 Essential Injection Molding Tooling Techniques for Efficient Production
Injection molding tooling plays a crucial role in the efficiency and effectiveness of the manufacturing process within various industries. As companies continue to seek innovative ways to enhance productivity while maintaining high-quality standards, understanding the essential techniques in injection molding tooling becomes increasingly vital. These techniques not only optimize production speed but also ensure precision in the final products, reducing waste and costs associated with defects.
In this article, we will delve into the top 10 essential injection molding tooling techniques that can significantly impact production outcomes. From the initial design phase to the final execution of molds, each technique will be explored in detail, highlighting best practices and strategies that manufacturers can implement. By mastering these techniques, businesses can streamline their operations, improve turnaround times, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge in the marketplace. Whether you are new to injection molding or looking to refine your existing processes, this guide aims to provide valuable insights that can lead to efficient and successful production outcomes.

Overview of Injection Molding Tooling Techniques for Efficient Production
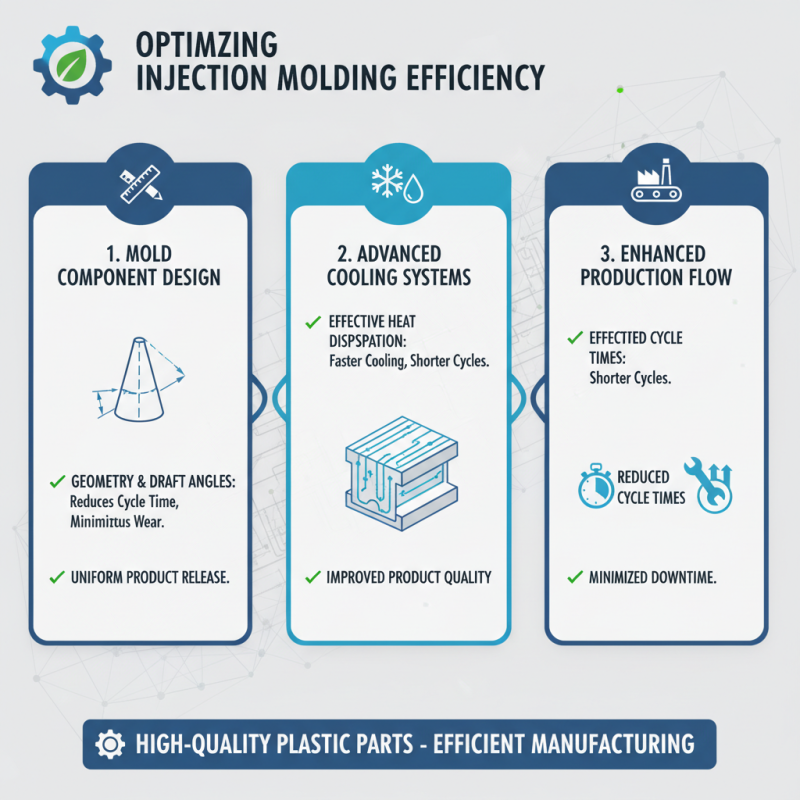
Injection molding is a critical process in the manufacturing industry, providing an efficient way to produce high-quality plastic parts. Understanding various tooling techniques can significantly enhance production efficiency. One essential technique is the proper design of mold components. By optimizing the geometry and ensuring sufficient draft angles, manufacturers can reduce cycle times and minimize wear on molds. This design process should also include considerations for cooling systems, as effective cooling leads to a more uniform product and shorter processing times.
Tips: Always ensure that cooling channels are strategically placed to allow for even heat distribution. This not only aids in reducing cycle times but also leads to improved part quality, preventing defects that might arise from uneven cooling.
Another crucial aspect is integrating automation into the injection molding process. Utilizing robotic arms for tasks such as part removal and assembly can streamline operations, reduce human error, and enhance productivity. Moreover, regular maintenance of molds and machines is essential to ensure optimal performance. Well-maintained equipment translates to consistent output and can prevent costly downtimes due to unexpected failures.
Tips: Schedule routine maintenance checks and implement a preventive maintenance program to identify wear and tear before it leads to significant issues. Keeping molds clean and properly lubricated will extend their lifespan and maintain production quality.
Key Factors Influencing Injection Molding Efficiency
Injection molding efficiency is influenced by several key factors that determine the overall success of the production process. Firstly, the design of the mold plays a critical role; it should allow for optimal flow of the molten material and minimize any potential defects. Effective cooling systems integrated into the mold can significantly enhance the cycle time by ensuring uniform temperature distribution. Additionally, the choice of materials not only affects the cost but also the performance characteristics, making it vital to select the right resin based on the intended application.
Moreover, the injection molding machine settings are crucial for achieving consistent results. Parameters such as injection speed, pressure, and temperature need to be meticulously optimized to prevent issues like warping or incomplete filling. Regular maintenance of the machinery and molds can also prevent downtime and maintain production efficiency. Finally, operator training and expertise in handling the machinery contribute significantly to the efficiency of the injection molding process, emphasizing the importance of skilled labor in achieving high-quality outputs.
Top 10 Essential Injection Molding Tooling Techniques for Efficient Production
Step-by-Step Guide to Designing Molding Tools
Designing effective molding tools is crucial for optimizing production efficiency in the injection molding process. A well-structured approach begins with a thorough analysis of the part design and material selection, as noted in the "2021 Injection Molding Industry Report," which emphasizes that up to 80% of manufacturing costs can be predetermined at the design stage. This highlights the significance of engaging in a collaborative design process that considers manufacturability, functionality, and cost-effectiveness.
When designing molding tools, it's essential to incorporate design for manufacturability (DFM) principles. This includes optimizing wall thickness, integrating features that facilitate ejection, and minimizing complex geometries. According to recent studies, molds with uniform wall thickness can reduce cycle times by 15-20%, leading to substantial cost savings. Using simulation tools such as flow analysis also aids in predicting potential defects, enabling engineers to refine the tool design before physical production begins.
**Tips**: Always aim for a balance between part complexity and tooling cost. Simplifying the mold design while maintaining the functionality can lead to lower production costs. Additionally, consider the choice of materials for the mold itself; high-quality steel can improve tool longevity and reduce maintenance needs, ultimately leading to fewer production downtimes. Regularly review and update your tooling design practices based on the latest industry advancements to stay competitive.
Top 10 Essential Injection Molding Tooling Techniques for Efficient Production
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Runner Systems | Utilizing heated channels to deliver molten plastic to the mold. | Improves cycle time and reduces waste of material. | Optimize temperature settings for material type. |
| Multiple Cavities | Designing molds with multiple cavities to produce several parts simultaneously. | Increased production efficiency and reduced per-unit costs. | Ensure uniform filling of cavities to avoid defects. |
| Core and Cavity Design | Creating intricate shapes by using cores and cavities in the mold. | Facilitates complex geometries and reduces machining time. | Evaluate part design for core and cavity complexity. |
| Ejector Systems | Mechanisms to remove the molded part from the mold. | Prevents damage to parts and ensures smooth production. | Select appropriate ejector design based on part geometry. |
| Cooling System Optimization | Improving the cooling channels for effective heat removal. | Reduces cycle time and improves part quality. | Simulate cooling patterns to ensure even heat distribution. |
| Material Selection | Choosing the right plastic material based on application requirements. | Enhances product performance and reduces defects. | Consider environmental impact and recycling potential. |
| Surface Finish Techniques | Applying finishes like polished or textured surfaces to molds. | Affects aesthetics and functionality of the final product. | Match finish type with product requirements. |
| Simulation and Analysis | Using software to predict flow and cooling patterns. | Identifies potential issues before mold creation. | Incorporate simulation early in the design phase. |
| Process Control | Implementing controls to monitor and adjust the molding process. | Ensures consistent quality and reduces scrap rates. | Use data analytics for real-time monitoring. |
| Feedback Loop for Continuous Improvement | Integrating feedback from production to improve tooling. | Enhances future designs and production efficiency. | Regular review meetings to assess tooling performance. |
Best Practices for Material Selection in Injection Molding
When it comes to injection molding, selecting the right materials is paramount for achieving efficiency and optimal performance in production. Start by considering the mechanical properties required for the final product, as these will influence material choice. Factors such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability are essential to ensure that the molded parts can withstand the intended application conditions. Moreover, understanding the flow characteristics of materials during the injection process can help in minimizing cycle times and maximizing output, which is particularly crucial in large-scale manufacturing.
Additionally, environmental considerations play a significant role in material selection. Using materials that are recyclable or have lower environmental impacts can enhance sustainability efforts within the production process. It’s also vital to assess compatibility with existing manufacturing techniques and equipment. Properly evaluating how materials interact with molds and considering their temperature and viscosity profiles can help in troubleshooting potential issues before they arise. By focusing on these best practices in material selection, manufacturers can streamline their injection molding processes, reduce waste, and ultimately improve product quality and production efficiency.
Future Trends in Injection Molding Tooling Techniques
As the injection molding industry evolves, emerging trends in tooling techniques are reshaping production efficiency. Recent industry reports indicate that advancements in automation and smart manufacturing are increasingly being integrated into the tooling process. For instance, a study by Mordor Intelligence projects that the automation market within injection molding will grow at a CAGR of over 5% from 2021 to 2026. This shift not only maximizes production speed but also enhances precision and reduces human error, ultimately leading to a decrease in scrap rates.
Another significant trend is the implementation of advanced materials in tooling construction. Innovations in materials, such as aluminum and new composite materials, are being adopted for their lightweight properties and durability. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the use of such materials can improve tooling lifespan by up to 50%, making the initial investment more cost-effective over time. Furthermore, these materials facilitate quicker heat transfer, which is critical for managing cycle times efficiently.
Tips: To remain competitive, manufacturers should consider investing in state-of-the-art simulation software. This technology allows for virtual testing of tooling designs before physical production, helping to identify potential issues early on. Additionally, participating in industry workshops can keep professionals informed about the latest techniques and materials, enabling them to implement best practices in their operations.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Selecting the Right Injection Molding Tooling for Your Business Needs
-

What is Low Cost Injection Molding and How it Revolutionizes Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Discovering the Secrets of Low Cost Injection Molding for Beginners
-

Innovative Injection Moulding Process Examples That Drive Global Procurement Efficiency
-

Injection Moulding Process Challenges That Every Global Buyer Should Know
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Low Cost Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Guide for Innovators
