10 Essential Tips for Designing Efficient Injection Molded Parts
In the rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, injection molded parts have become a cornerstone in various industries, ranging from automotive to consumer goods. According to recent industry reports, the global injection molding market was valued at approximately $234 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $360 billion by 2027, reflecting a substantial compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6%. This growth signifies the escalating demand for high-quality, efficient molded components that meet stringent performance and cost criteria.

To harness the full potential of injection molding, designers must focus on optimizing their design processes. Effective design not only enhances product performance but also plays a crucial role in minimizing waste and reducing production costs. Studies indicate that up to 70% of product costs can be determined at the design stage, underscoring the importance of thoughtful design strategies in the injection molding process. By implementing best practices and innovative techniques, companies can significantly improve the manufacturability and sustainability of their injection molded parts, thereby achieving a competitive edge in the marketplace.
This article presents 10 essential tips for designing efficient injection molded parts, aimed at guiding engineers and designers to maximize the advantages of this versatile manufacturing method.
Understanding Material Selection for Injection Molded Parts
When designing efficient injection molded parts, material selection is a critical factor that can significantly influence the performance and manufacturability of the final product. Different materials offer varying properties such as strength, flexibility, thermal resistance, and chemical stability, which must be matched to the part’s intended application. For instance, polycarbonate is an excellent choice for parts requiring impact resistance, while polyethylene is favored for its chemical resistance and low-cost characteristics. Understanding the specific demands of the application will help in choosing the right material that balances performance with cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, it's important to consider the material's flow characteristics during the injection molding process. Materials that flow easily under heat and pressure can lead to smoother finishes and more intricate designs. However, one must also weigh factors like shrinkage, viscosity, and cooling rates. Selecting the right resin not only improves the quality of the molded parts but also enhances the overall efficiency of the production process by minimizing defects and reducing cycle times. Engaging with material specialists and leveraging simulation tools can assist designers in making informed decisions to optimize both the design and functionality of injection molded components.
Optimizing Part Geometry for Enhanced Mold Performance
When designing efficient injection molded parts, optimizing part geometry is crucial for improving mold performance. A well-considered geometry not only enhances the aesthetic and functional aspects of the part but also plays a significant role in manufacturing efficiency and quality. To achieve this, designers should focus on maintaining uniform wall thickness throughout the part. This minimizes warping and reduces the risk of defects during the cooling process, leading to a more reliable final product.
Another essential tip is to incorporate features such as ribs and gussets strategically. These enhancements can strengthen the structure of the part without adding significant weight or complexity. Additionally, incorporating draft angles is vital for ensuring that parts eject easily from the mold. A good practice is to establish a draft angle of at least 1-2 degrees, which helps prevent damage to both the part and the mold itself during the ejection phase.
Furthermore, consider the use of fillets at corners and edges to distribute stress evenly and improve flow during material injection. This design tweak can substantially reduce the likelihood of defects, promoting a smoother manufacturing process overall. By keeping these geometry optimization strategies in mind, designers can significantly boost the efficiency and performance of their injection molded parts.
10 Essential Tips for Designing Efficient Injection Molded Parts
This chart illustrates the effectiveness score of various essential tips for designing efficient injection molded parts. Scores range from 1 to 10, showcasing the impact of each tip on improving mold performance.
Incorporating Draft Angles and Tolerances in Design
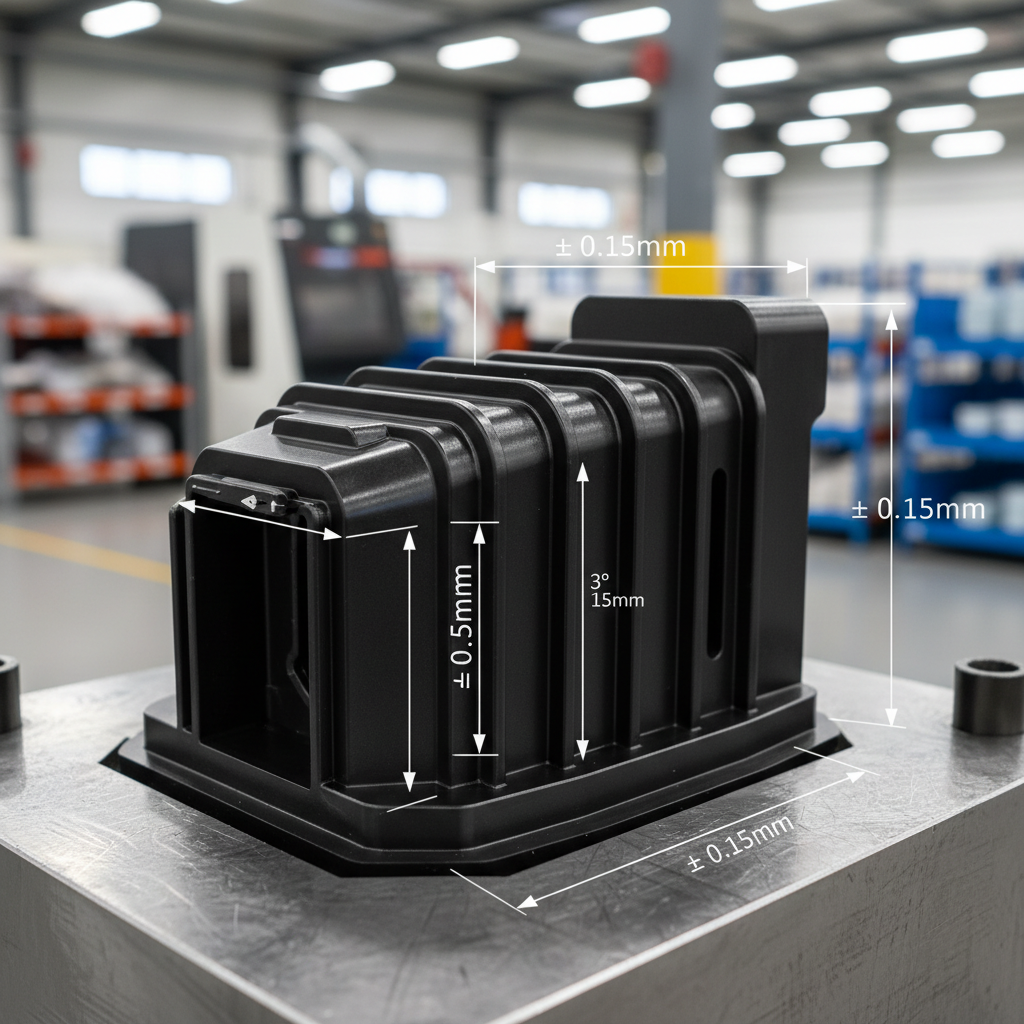

When designing injection molded parts, incorporating draft angles and tolerances is crucial for ensuring manufacturability and optimizing performance. Draft angles, typically ranging from 1 to 5 degrees, allow for easy release of parts from the mold, preventing potential damage and reducing cycle times. Properly designed draft angles not only facilitate smoother extraction but also minimize wear on the mold itself, which can lead to increased longevity and cost savings over time.
Tolerances play an equally significant role in injection molding. Achieving the right tolerances ensures that parts fit together as intended, essential for maintaining the integrity of the final assembly. It's important to recognize that tighter tolerances can lead to increased production costs and longer cycle times. Therefore, balancing functionality with manufacturability is key. Designers should assess the part's function and determine the minimum necessary tolerances to optimize both performance and production efficiency.
By integrating effective draft angles and carefully considering tolerances during the design phase, manufacturers can significantly enhance the overall quality and success of their injection molded components.
Evaluating Cooling Systems for Efficient Mold Cycle Times
When designing injection molded parts, evaluating the cooling systems is critical for optimizing mold cycle times. A well-designed cooling system ensures uniform temperature distribution and reduces the time required for the material to solidify, allowing for faster production rates. To achieve this, it's essential to utilize tools like computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to simulate coolant flow and predict how heat will dissipate throughout the mold. This proactive approach can significantly enhance mold performance and efficiency.
One key tip is to prioritize the placement of cooling channels. Channels should be strategically located to minimize the length and maximize the surface area in contact with the part. Additionally, consider using conformal cooling channels that can follow the contours of the molded part to improve heat transfer. This allows for a more consistent cooling process, reducing warpage and defects, thus streamlining production.
Another important consideration is the coolant's temperature and flow rate. Implementing a closed-loop cooling system can help maintain optimal temperatures, while a balanced flow rate ensures that all areas of the mold cool evenly. Monitoring and adjusting these variables can lead to substantial improvements in cycle times, resulting in higher efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Testing and Prototyping: Essential Steps Before Final Production
Prototyping and testing are critical steps in the design process of injection molded parts, ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements. Before moving to final production, creating prototypes allows designers to evaluate their designs in real-world scenarios. This stage aids in identifying potential issues early on, such as improper fit, structural weaknesses, or challenges in manufacturing. Utilizing rapid prototyping techniques, like 3D printing, can significantly accelerate this phase, enabling quick iterations based on feedback.
Moreover, thorough testing is essential to validate the performance and durability of the prototypes. This process includes assessing mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental factors. Conducting tests under controlled conditions helps ensure that the final part can withstand its intended usage. Emphasizing these steps in the development process not only reduces risk but also improves overall efficiency in producing injection molded parts, ultimately leading to a more reliable end product.
Related Posts
-

Injection Moulding Process Challenges That Every Global Buyer Should Know
-

How to Optimize PVC Injection Molding for Maximum Efficiency and Quality
-

Exploring the Future of Injection Molding at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Insights and Growth Projections
-
Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Future of Plastic Injection Molding Technologies
-

Top 10 Benefits of Injection Molding for Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Revolutionizing Product Design with Innovative PVC Injection Molding Techniques
